Republic of Korea
|
Economy Detail
1. Laws of Metrology
1.1 Legal requirements for traceability
The Framework Act on National Standards requires that the measurement of physical quantity for legal purpose be made by means of, reference to, comparison with, or derived from specified standards of measurement including certified reference materials.
The Framework Act on National Standards requires that the measurement of physical quantity for legal purpose be made by means of, reference to, comparison with, or derived from specified standards of measurement including certified reference materials.
2. Legal Units of Measurement
The legal units of measurement are defined in the Presidential Decree of the Framework Standards Act on National Standards and are those of the International System of Units (SI). The unification of all measuring units into the metric system began in 1964 excluding the fields of land and building, and the SI units constituted as the legal units since January 1st, 1983 including the fields of land and building with limited exceptions for cases shown below:
-A measuring instrument used to measure export products or products imported for re-export;
-A measuring instrument used to measure ships, airplanes, or commodities for military purposes;
-A measuring instrument used to measure commodities utilized for research and development;
-A measuring instrument or product for export;
-A measuring instrument or product imported as raw materials or components of export products.
-A measuring instrument used to measure export products or products imported for re-export;
-A measuring instrument used to measure ships, airplanes, or commodities for military purposes;
-A measuring instrument used to measure commodities utilized for research and development;
-A measuring instrument or product for export;
-A measuring instrument or product imported as raw materials or components of export products.
3. Structure of Metrological Control Authorities
3.1 National organization for legal metrology
Korean Agency for Technology and Standards (KATS)
Ministry of Trade, Industry and Energy (MOTIE)
93 Isu-ro, Maengdong-myeon, Eumseong-gun, Chungcheongbuk-do, 369-811, Republic of Korea
KATS is responsible for the following:
-completing the metric system;
-establishment and coordination of metrological policy on all aspects of the National Measurement System;
-maintenance and dissemination of the physical standards of measurement for Korean legal units of measurement through KRISS; and
- supervision (or guidance) over its subordinate organizations on matters relating to legal metrology and the use of legal units of measurement.
This body is directly responsible for OIML activities.
3.2 Custodian of National Standards
The Custodian of national standards of measurement is the Korea Research Institute of Standards and Science (KRISS):
KRISS
267 Gajeong-ro, Yuseong-gu, Daejeon 34113, Republic of Korea
Tel. +82.42.868.5114
Fax +82.42.868.5252
The major functions and roles of KRISS are as follows:
3.3 National organizations responsible for maintaining primary standards
KRISS is the national organization responsible for maintaining primary standards.
3.4 Regional and local verification organizations
Regional and local verification organizations are the head office and 5 regional branch offices of Korea Testing Certification (KTC). However, the organizations responsible for reverification are each regional governmental office.
3.5 Instrument calibration and evaluation systems
Calibration on measuring instruments is performed by accredited calibration laboratories. The Korea Laboratory Accreditation Scheme (KOLAS) is a national accreditation body established under Korean Agency for Technology & Standards (KATS) to accredit the calibration laboratories in accordance with the KOLAS regulations, ISO/IEC 17025 and ISO/IEC 17020, and to evaluate the technical and operational competence of laboratories to perform calibration.
Korean Agency for Technology and Standards (KATS)
Ministry of Trade, Industry and Energy (MOTIE)
93 Isu-ro, Maengdong-myeon, Eumseong-gun, Chungcheongbuk-do, 369-811, Republic of Korea
KATS is responsible for the following:
-completing the metric system;
-establishment and coordination of metrological policy on all aspects of the National Measurement System;
-maintenance and dissemination of the physical standards of measurement for Korean legal units of measurement through KRISS; and
- supervision (or guidance) over its subordinate organizations on matters relating to legal metrology and the use of legal units of measurement.
This body is directly responsible for OIML activities.
3.2 Custodian of National Standards
The Custodian of national standards of measurement is the Korea Research Institute of Standards and Science (KRISS):
KRISS
267 Gajeong-ro, Yuseong-gu, Daejeon 34113, Republic of Korea
Tel. +82.42.868.5114
Fax +82.42.868.5252
The major functions and roles of KRISS are as follows:
- to establish, maintain and disseminate the national measurement standards through systematic calibration
- to conduct research and development in the field of measurement science and precision technology
- to provide education and training in measurement standards,etc.
3.3 National organizations responsible for maintaining primary standards
KRISS is the national organization responsible for maintaining primary standards.
3.4 Regional and local verification organizations
Regional and local verification organizations are the head office and 5 regional branch offices of Korea Testing Certification (KTC). However, the organizations responsible for reverification are each regional governmental office.
3.5 Instrument calibration and evaluation systems
Calibration on measuring instruments is performed by accredited calibration laboratories. The Korea Laboratory Accreditation Scheme (KOLAS) is a national accreditation body established under Korean Agency for Technology & Standards (KATS) to accredit the calibration laboratories in accordance with the KOLAS regulations, ISO/IEC 17025 and ISO/IEC 17020, and to evaluate the technical and operational competence of laboratories to perform calibration.
4. Range of Equipment Subject to Legal Metrology
Under the Measures Act, measuring instruments are divided into two categories. The first category is measuring instruments for trade or certification purposes, which are 12 items (non-automatic weighing instruments, weights, gas meters, water meters, hot water meters, oil meters, fuel dispenser, urea water meters, LPG meters, graduated tanks, heat meters and electricity meters)as prescribed by the Presidential Decree. The second category is measuring instruments for measurement except for trade or certification. Two categories are the same in a sense that these instruments are machines, appliances or devices for measurement of the quantity of the state of physical phenomena.
5. Type Approval
5.1 Legal and technical requirements for type approval
Korean Agency for Technology and Standards (KATS) has the responsibility for the type approval in accordance with the Measures Act and KATS has delegated the authority to the Korea Testing Certification (KTC).
KTC carries out this responsibility by examining the designs of measuring instruments and testing sample instruments. Once the type of an instrument has been approved, KTC issues a certificate of approval and instruments made to the type must be marked with KTC number contained in that certificate. The marking of this number on the instruments is the primary indication that the measuring instruments are of an approved type.
Type approval requirements are contained in the standards of verification by the Order of the Administrator.
5.2 Authority responsible for issuing type approval
KTC is the authority responsible for issuing type approval certificates for the measuring instruments for use of trade or certification as prescribed by the Ordinance of the Ministry of Commerce, Industry and Energy (hereinafter referred to as “The Ordinance of the Ministry”).
5.3 Recognition/acceptance of OIML certificates
Republic of Korea is currently a Utilizer of OIML Certification System. KATS delegated Issuing Authority and Testing Laboratory authority to KTC, which is a type approval and verification institute in Republic of Korea.
5.4 Authority responsible for testing for type approval
KTC (Korea Testing Certification) is the authority responsible for testing for type approvals.
5.5 List of major test facilities available
The principal testing facilities operated by KTC are;
5.6 Fee structure
Fees vary according to the type of component or instrument to be tested.
Typical examination fees, for example, are as follows;
Korean Agency for Technology and Standards (KATS) has the responsibility for the type approval in accordance with the Measures Act and KATS has delegated the authority to the Korea Testing Certification (KTC).
KTC carries out this responsibility by examining the designs of measuring instruments and testing sample instruments. Once the type of an instrument has been approved, KTC issues a certificate of approval and instruments made to the type must be marked with KTC number contained in that certificate. The marking of this number on the instruments is the primary indication that the measuring instruments are of an approved type.
Type approval requirements are contained in the standards of verification by the Order of the Administrator.
5.2 Authority responsible for issuing type approval
KTC is the authority responsible for issuing type approval certificates for the measuring instruments for use of trade or certification as prescribed by the Ordinance of the Ministry of Commerce, Industry and Energy (hereinafter referred to as “The Ordinance of the Ministry”).
5.3 Recognition/acceptance of OIML certificates
Republic of Korea is currently a Utilizer of OIML Certification System. KATS delegated Issuing Authority and Testing Laboratory authority to KTC, which is a type approval and verification institute in Republic of Korea.
5.4 Authority responsible for testing for type approval
KTC (Korea Testing Certification) is the authority responsible for testing for type approvals.
5.5 List of major test facilities available
The principal testing facilities operated by KTC are;
- Automated load cell testing facilities
- Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC) testing facility
- Non-automatic weighing instrument testing facility
- Liquid Petroleum Gas (LPG) testing facility
- Thermometer testing facility
- Water meter (smaller than 150 mm in diameter) testing facility
- Temperature controlled chamber for environmental testing facility
- Electricity meter testing facility
5.6 Fee structure
Fees vary according to the type of component or instrument to be tested.
Typical examination fees, for example, are as follows;
- Non-automatic weighing instruments : 2,516,200 Won
- Weights : 445,390 Won
- Gas meter : 5,315,850 Won
- Water meter : 2,552,860 Won
- Hot water meter : 2,474,170 Won
- Oil meter : 2,719,720 Won
- Fuel dispenser : 2,601,230 Won
- Urea water meter : 2,439,040 Won
- LPG meter : 2,245,850 Won
- Gradated tank : 569,420 Won
- Heat meter : 4,829,010 Won
- Electricity meter : 10,237,240 Won
6. Verification (Conformity Assessment), Inspection and Reverification
6.1 Legal and technical requirements for verification and reverification
The Administrator of KATS has the verification authority for the measuring instruments prescribed by the Presidential Decree. The Administrator of KATS prescribes the verification criteria and may designate specialized institute for the verification.
The measuring instruments that must be verified in accordance with the provisions of the Presidential Decree are as follow:
6.2 Range of equipment verified and reverified and any statistical information available
Measuring instruments verified are indicated in clause 6.1 above. Measuring instruments’ validity terms are as follows:
The above-mentioned measuring instruments shall be re-verified when the validity term is expired. It is regulated that any other measuring instruments that the term of validity is not defined above shall be verified every two years regularly by the governor of Province. In addition, the measuring instruments beyond the permissible errors shall be repaired or withdrawn.
6.3 Fee structure
Fees vary in accordance with the type of component or instrument to be verified.
The Administrator of KATS has the verification authority for the measuring instruments prescribed by the Presidential Decree. The Administrator of KATS prescribes the verification criteria and may designate specialized institute for the verification.
The measuring instruments that must be verified in accordance with the provisions of the Presidential Decree are as follow:
- Non-automatic weighing instruments(3 items)
- Weights (2 items)
- Gas meters
- Water meters
- Hot Water meters
- Oil meters
- Fuel dispensers
- Urea water meters
- LPG meters
- Graduated tanks
- Heat meters
- Electricity meters
6.2 Range of equipment verified and reverified and any statistical information available
Measuring instruments verified are indicated in clause 6.1 above. Measuring instruments’ validity terms are as follows:
- Non-automatic weighing instrument : 2 years
- Gas meter : 5 ~ 8 years
- Water meter : 6 ~ 8 years
- Hot water meter : 6 years
- Oil meter : 5 years
- Fuel dispenser : 2 years
- LPG meter: 3 years
- Heat meter : 5 years
- Electricity meter : 7 ~ 15 years
The above-mentioned measuring instruments shall be re-verified when the validity term is expired. It is regulated that any other measuring instruments that the term of validity is not defined above shall be verified every two years regularly by the governor of Province. In addition, the measuring instruments beyond the permissible errors shall be repaired or withdrawn.
6.3 Fee structure
Fees vary in accordance with the type of component or instrument to be verified.
- Non-automatic weighing instruments : 70 ~ 112,460 Won
- Gas meter : 130 ~ 33,710 Won
- Water meter : 170 ~ 21,250 Won
- Hot water meter : 170 ~ 21,250 Won
- Oil meter : 3,460 ~ 25,480 Won
- Fuel dispenser : 14,300 Won
- LPG meter : 23,180 Won
- Heat meter : 1,120 ~ 47,670 Won
- Electricity meter : 420 ~ 5,830 Won
7. Accreditation and Certification Systems
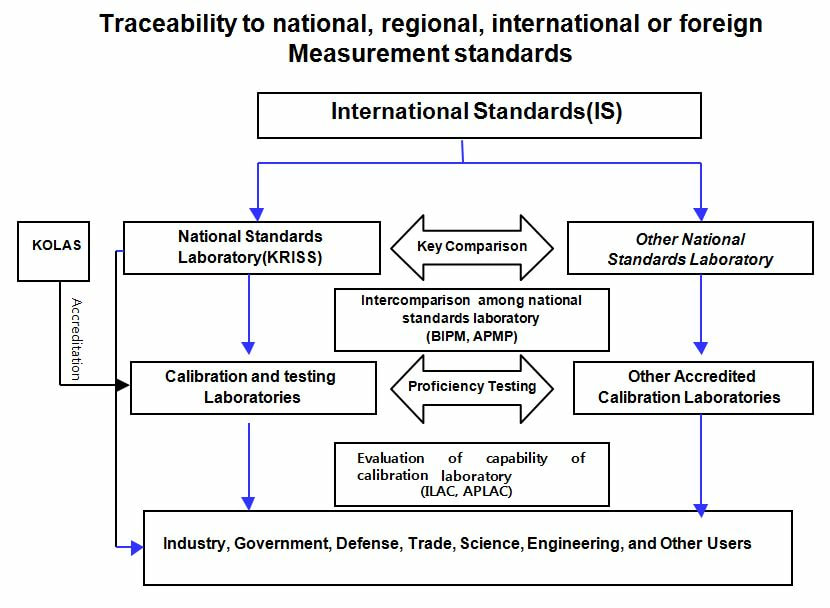
7.1 Accreditation systems for legal metrology, calibration and testing laboratories. Traceability to national, regional, international or foreign measurement standards
The Korea laboratory Accreditation Scheme (KOLAS) is a national accreditation body established under Korean Agency for Technology and Standards(KATS) to evaluate the technical and operational competence of laboratories and inspection bodies to perform tests, calibration and/or inspection in a certain field, and accredit them in accordance with the KOLAS regulations, ISO/IEC 17025 and ISO/IEC 17020.
Currently, 219 calibration laboratories and 547 testing laboratories have been accredited in accordance with the requirement of ISO/IEC 17025 by KOLAS. KOLAS represents Korea on the International Laboratory Accreditation Cooperation (ILAC) and is also the signatory of ILAC-MRAs.
The Korea laboratory Accreditation Scheme (KOLAS) is a national accreditation body established under Korean Agency for Technology and Standards(KATS) to evaluate the technical and operational competence of laboratories and inspection bodies to perform tests, calibration and/or inspection in a certain field, and accredit them in accordance with the KOLAS regulations, ISO/IEC 17025 and ISO/IEC 17020.
Currently, 219 calibration laboratories and 547 testing laboratories have been accredited in accordance with the requirement of ISO/IEC 17025 by KOLAS. KOLAS represents Korea on the International Laboratory Accreditation Cooperation (ILAC) and is also the signatory of ILAC-MRAs.
7.2 Legal and applied metrological activities in products certification
KS (Korean Industrial Standards) Mark Scheme is operated by KATS. When the applicant company’s quality system complies with the assessment criteria, and the quality of the product conforms to the relevant Korean Industrial Standards, the company is granted the right to use the Mark.
7.3 Legal and applied metrological activities in ISO 9000 quality management systems
Korea adopted the ISO 9000 series as Korean Industrial Standards in 1992 as the KS A 9000 series.
KS (Korean Industrial Standards) Mark Scheme is operated by KATS. When the applicant company’s quality system complies with the assessment criteria, and the quality of the product conforms to the relevant Korean Industrial Standards, the company is granted the right to use the Mark.
7.3 Legal and applied metrological activities in ISO 9000 quality management systems
Korea adopted the ISO 9000 series as Korean Industrial Standards in 1992 as the KS A 9000 series.
8. Legal Metrology Practitioners
8.1 Numbers
The approximate number of people involved in the field in Korea is as follows:
8.2 Qualification/training
The qualifications for legal metrology practioners are the following as;
8.3 Training organizations and courses organised
Korea Association of Standards and Testing Organizations (KASTO), formed in 1990 to promote effective operation of the national calibration service and close cooperation conducts the following courses;
8.4 Range of functions
KATS is responsible for establishing and revising the Measures Act and verification criteria.
KTC is a type approval and verification body for 12 measuring instruments including oil meters, electricity meters, etc and KTL is a type approval body for electricity meter.
Governors in province are responsible for re-verification of measuring instruments, inspection of in-use measuring instruments (periodical inspection) and inspection of prepackaged products.
The approximate number of people involved in the field in Korea is as follows:
- 10 officers in Metrology & Measurement Division of KATS
- 30 officers involved in testing and type approval functions at KTC
- 80 engineers for verification at KTC
- Approximately 200 local technical officers for reverification and inspection at 16 local Governments
8.2 Qualification/training
The qualifications for legal metrology practioners are the following as;
- Those who hold the certificate of the relevant areas
- Those who complete the training courses concerned, by the training organizations designated by KATS
8.3 Training organizations and courses organised
Korea Association of Standards and Testing Organizations (KASTO), formed in 1990 to promote effective operation of the national calibration service and close cooperation conducts the following courses;
- Legal Metrology Technical officer’s course,
- Advanced Measurement training course,
- Understanding of KS Q ISO/IEC 17025,
8.4 Range of functions
KATS is responsible for establishing and revising the Measures Act and verification criteria.
KTC is a type approval and verification body for 12 measuring instruments including oil meters, electricity meters, etc and KTL is a type approval body for electricity meter.
Governors in province are responsible for re-verification of measuring instruments, inspection of in-use measuring instruments (periodical inspection) and inspection of prepackaged products.
9. Packaging
9.1 Legislative control for packaging
Measures Act and the Presidential Decree specify the accuracy and the marking of prepackaged products, which must conform to packaging control.
9.2 Organization responsible
The mayors or governors of 17 provinces have the responsibility for prepackaged products as prescribed in the Presidential Decree.
Measures Act and the Presidential Decree specify the accuracy and the marking of prepackaged products, which must conform to packaging control.
9.2 Organization responsible
The mayors or governors of 17 provinces have the responsibility for prepackaged products as prescribed in the Presidential Decree.
10. Sanctions
Under the Measures Act, the main penalties are as follows;
10.1. Imprisonment for up to three years, or a fine of not exceeding 30 million Won
10.3. Imprisonment for up to one year, or a fine of not exceeding 10 million Won
10.4. Fine of not exceeding 3 million Won
10.5. Fine of not exceeding 1 million Won
10.1. Imprisonment for up to three years, or a fine of not exceeding 30 million Won
- A person who transfers or leases any measuring instrument altered differently from type approval therefor or advertises such measuring instrument for the purpose of transfer or lease
- A person who uses any measuring instrument the transfer or leasing of which and advertisements for the transfer or leasing of which are restricted
- A person who alters any measuring instrument for the purpose of changing the value of measurement or uses any altered measuring instrument
- A person who uses any measuring instrument with knowledge of the fact that it was altered inconsistently with type approval therefor
- A person who arbitrarily removes the mark of prohibition of use or uses any measuring instrument from which such mark has been removed
- A person who manufactures or repairs measuring instruments not registered
- A person who repairs measuring instruments although he/she is not a designated self-repairing dealer
- A person who imports measuring instruments without filing a report thereon
- A person who indicates a type approval number or other similar mark on any measuring instrument not type-approved (referring to measuring instruments type approval for which has been revoked after obtaining type approval)
- A person who destroys the labelling of a type approval number
- A person who destroys a verification mark or other seal for the purpose of altering any measuring instrument
- A person who conducts regular inspections of measuring instruments despite not having been designated as a dealer capable of conducting regular self-inspection
- A person who transfers or leases any measuring instrument which is not type-approved or advertises such measuring instrument for the purpose of transfer or lease thereof
- A person who transfers or leases any measuring instrument which has not undergone verification or advertises such measuring instrument for the purpose of transfer or lease thereof
- A person who transfers or leases any measuring instrument to which no verification mark or inspection mark has been affixed or to which a false mark is affixed, or advertises such measuring instrument for the purpose of transfer or lease thereof
- A person who uses any measuring instrument the transfer or lease of which or advertisements for the transfer or leasing of which are restricted
- A person who uses any measuring instrument with knowledge of the fact that it is type-approved falsely
- A person who uses any measuring instrument with knowledge of the fact that the relevant measuring instrument is affixed with a false verification mark or inspection mark
- A person who indicates the self-declaration of conformity or other similar ones
10.3. Imprisonment for up to one year, or a fine of not exceeding 10 million Won
- A person who manufactures or imports any measuring instrument marked in nonlegal units
- A person who fails to execute an order to mark legal units, an order to label the net quantity, or a request for correcting a labelling
- A person who runs the business of measurement and certification without registering his/her business
- A person who fails to execute a corrective order
- A person who fails to indicate, or falsely indicate, the maximum permissible error, etc
- A person who fails to label the net quantity or labels the quantity marked on a relevant product and the actual quantity in excess of the permissible error
- A person who fails to remove a labelling of the self-declaration of conformity
10.4. Fine of not exceeding 3 million Won
- A person who manufactures or imports any product marked in non-legal units
- A person who fails to make public any defect of a measuring instrument or does so falsely
- A person who transfers or leases measuring instruments marked in non-legal units or advertises such measuring instruments for the purpose of transfer or lease
- A person who uses any measuring instrument the transfer or lease of which or advertisements for the transfer or lease of which are restricted
- A person who uses any measuring instrument in excess of the error of usage
- A person who takes measurements in excess of the error of usage
10.5. Fine of not exceeding 1 million Won
- A person who uses nonlegal units for measurement or advertisements
- A person who fails to report on results
- A person who fails to report on changes
- A person who fails to preserve relevant records
- A person who fails to file a report on discontinuance of business, etc
- A person who fails to preserve relevant records
- A person who fails to make a report on the plans for, progress and result of, corrective measures
- A person who uses any measuring instrument, the period of validity of which has elapsed without having such measuring instrument re-verified
- A person who fails to preserve relevant records
- A person who transfers or leases any measuring instrument, the period of validity of verification of which or the period of validity of re-verification of which has elapsed, or advertises such measuring instrument for the purpose of transfer or lease
- A person who transfers or leases any measuring instrument which is not marked with the maximum permissible error, etc. or marked falsely, or advertises such measuring instrument for the purpose of transfer or lease
- A person who uses any repaired measuring instrument which has failed to undergo re-verification
- A person who uses any measuring instrument which has failed to undergo regular inspection
- A person who uses any measuring instrument the transfer or lease of which or advertisements for the transfer or lease of which are restricted